Why Renamag is different
The Bio-availability and GI friendly side effect profile are due to the lack of hydration shell that other magnesiums form during digestion as well as the pH at which Renamag absorbs.
It starts in the stomach
-

Most magnesium is soluble in the acidic enviromenment of the stomach. This is due to most Mg having only one bond to its component acid. The magnesium in Renamag, magnesium glycerophosphate is less soluble in the acidic environment of the stomach because it is bound at two points, one bond to glycerol and one bond to phosphoric acid.
While stomach solubility sounds good, it is the first step in causing magnesium to be less-bioavailable and to have a laxative effect.
The creation of the hydration shell
-

Most magnesiums in the dissolved state after being exposed to the acidic environment in the stomach have an extreme atrraction to water. The magnesium becomes surrounded in water in what is called a hydration shell.
-

The addition of the hydration shell can cause the compound to become 400X larger than the non-hydrated magnesium. The large compound now has reduced bioavailability due to its size being too large to pass through the intestinal epithilia.
-

Renamag with its 2 point bond better survives the stomach intact without the creation of a hydration shell.
The hydration shell reduces absorption and introduces bound water into the bowel.
-
Column
Pair text with an image to focus on your chosen product, collection, or blog post. Add details on availability, style, or even provide a review.
-
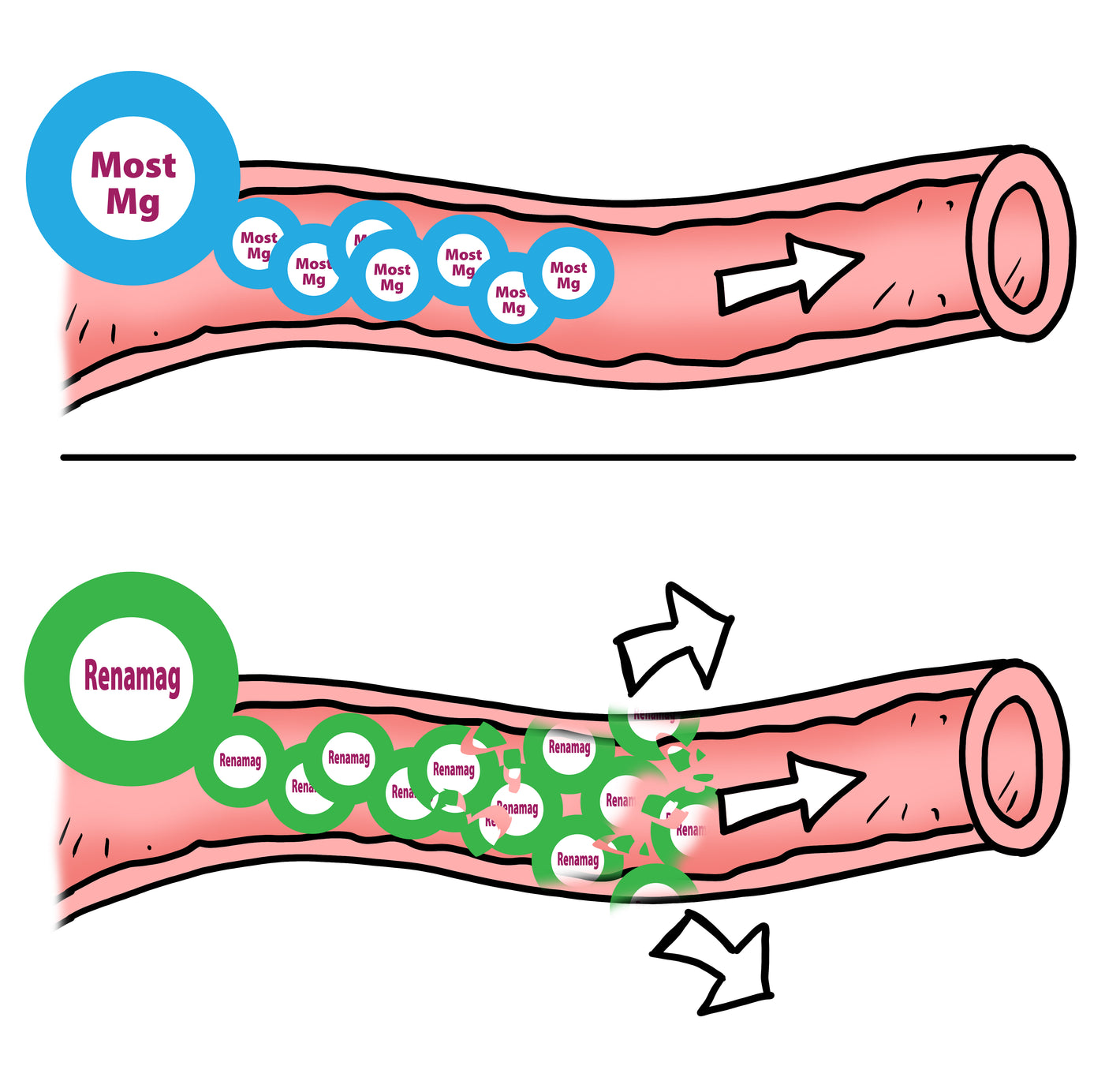
The Mg with the hydration shell is now a larger molecule that has less bioavalability. The compound has a harder time crossing the membrane of intestinal wall to be absorbed and utilized for physical function. The Mg molecule with bound water then travels thru the GI tract picking up more water via osmosis causing the common laxitive effect.
Renamag is still unbound to water in the small intestine and can more easilty pass through the epithilial wall and into the bloodstream.
Renamag absorbs at intestinal pH
-

The pH at which Renamag dissolves is also one of it's benefits.
While other magnesiums dissolve in the acid environment of the stomach, Renamag dissolves in the pH environment of the small intestine making it more bioavailable.
The end result.
-

Most Magnesium
With most magnesium supplementation, magnesium levels remain frustratingly and some times dangerously low, while GI side effect may negatively impact the patients life experience.
-

Renamag
What matters most is the end result. With Renamag the pateint has the chance to live without the side effects of low magnesium levels and without the laxative side effect seen with most magnesium supplementation.
GI Side Effect Comparison
Bioavailability comparison
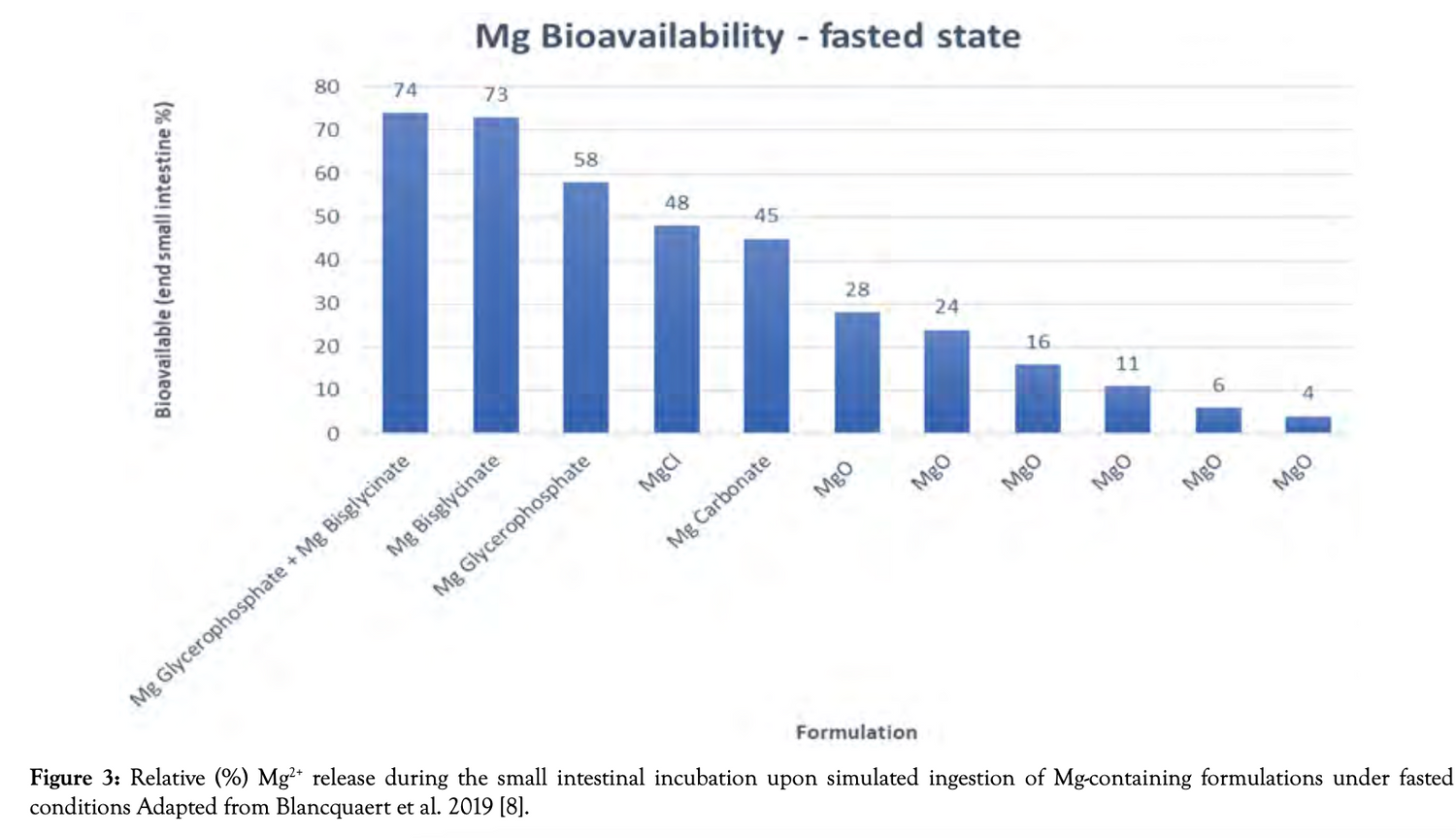
Bioavailability fasting
Link to publication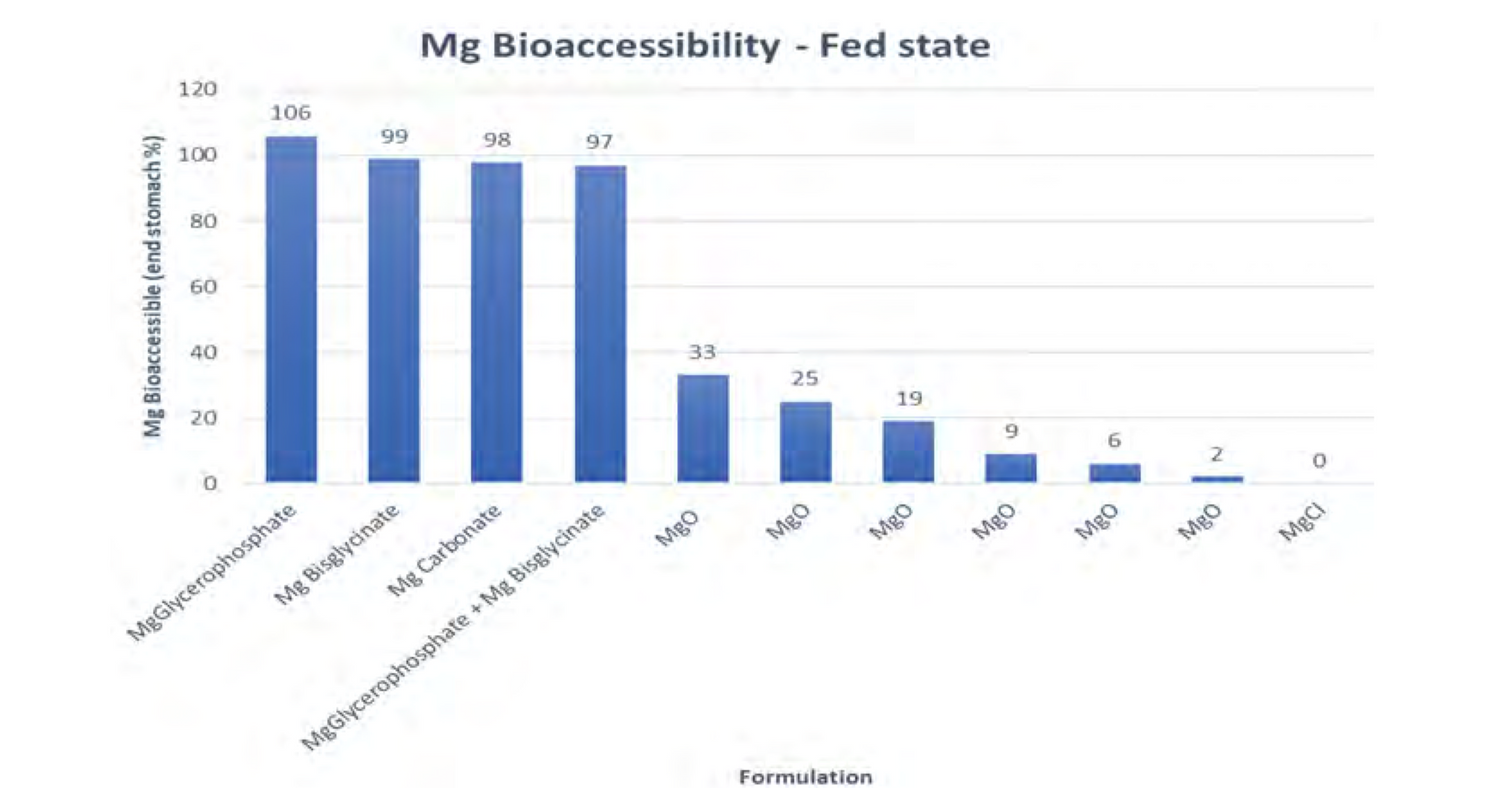
Bioavailability fed
Link to publication
Renamag dosing conversion
There are many factors that can affect the absorption and tolerability of various magnesium salts. This said, below is a general conversion from magnesium oxide to Renamag/magnesium glycerophosphate.
Mg glycerophosphate bioavailability 60%
Mg oxide Bioavailability 15%
- Renamag dose of two 425mg capsules = 100mg elemental Mg x 60% = 60mg Mg
- Mg oxide 400 mg =244mg elemental Mg x 15% = 37mg Mg
Renamag dosing per NHS Guidelines
-

-
Magnesium Glycerophosphate in the UK
In the UK where Mg Glycerophosphate has been available for over 10 years, it carries guideline support, formulary inclusion and dosing is protocolized in many of the NHS systems. Please see the Guideline section of this site for more information.
Below are some samples of formulary inclusions and publications including magnesium glycerophosphate.
-

-

The clinical data.
Driessens E.C. et al; On formulas for daily oral magnesium supplementation and some of thier side effects. Magnesium Bulletin 15 1 (1993)
L Blancquaert, C Vervaet et al; Predicting and testing bioavailability of Magnesium Supplements - Nutrients, 2019
Public Assessmeent Report UKPAR Neomag 4 mmo; chewable tablets 2017
Lewis R.V. et al; Oral magnesium reduces ventricular ectopy in digitalised patients with chronic atrial fibrillation. EJ of Clni. Pharmacology. 38 107-110 (1990)
Vynckier An-Katrien et al; Type of Magnesium Salt and Formulation Solubility Determines Bioavailability of Magnesium Food Supplements.J of Food Science and Nutrition. Vol 10, 2020
Patients not appropriate for Renamag.
Renamag should not be used in patinets with a GFR <30ml/min
Renamag should not be used in patients with hyperphosphatemia due to Renamag containing phosphoric acid.
Renamag is a medical Food
Unlike supplements a medical food, as defined in section 5(b)(3) of the Orphan Drug Act (21 U.S.C. 360ee(b)(3)), is “a food which is formulated to be consumed or administered enterally under the supervision of a physician and which is intended for the specific dietary management of a disease or condition for which distinctive nutritional requirements, based on recognized scientific principles, are established by medical evaluation.” Medical Foods, including Renamag can be purchased OTC without a prescription. Renamag is made in the USA in an FDA inspected facility under cGMP guidelines.



















